Cross the epithelial basement membrane in both basal to apical and apical to basal directions. Basal lamina and reticular lamina.
Epithelial Tissue Muscle Tissue Nervous Tissue Con Chegg Com
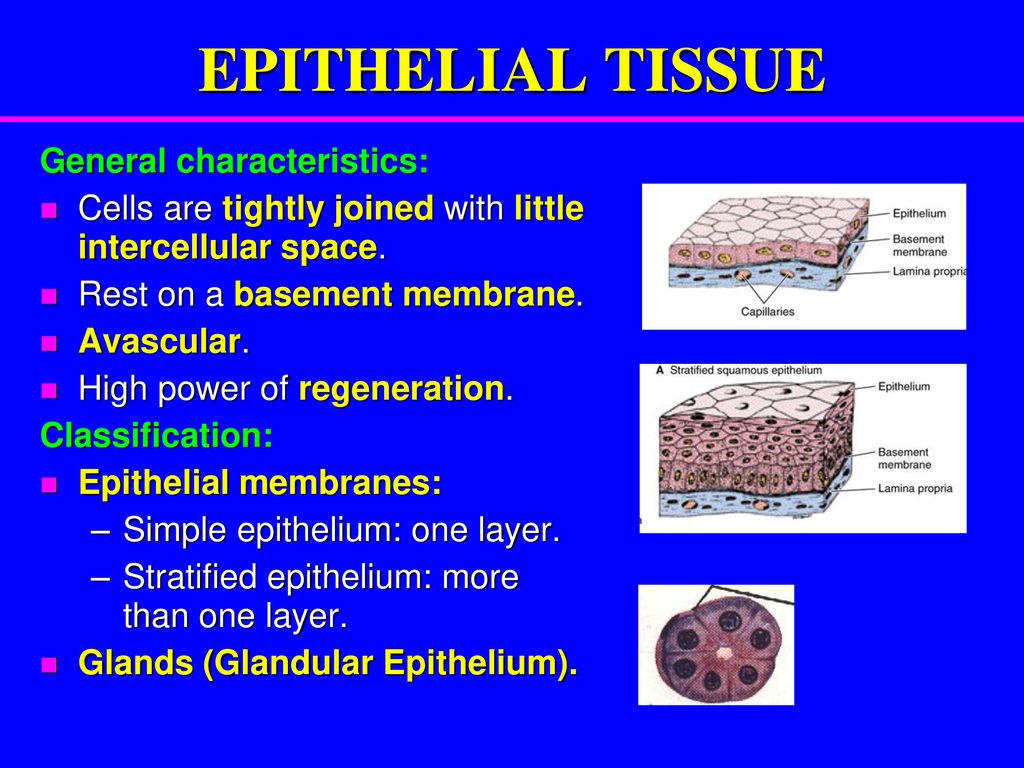
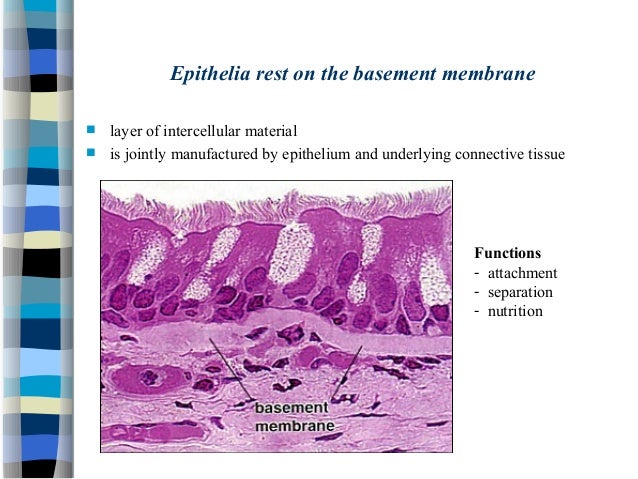
Most epithelial cells are separated from the connective tissue by a sheet of extracellular material called basement membrane.
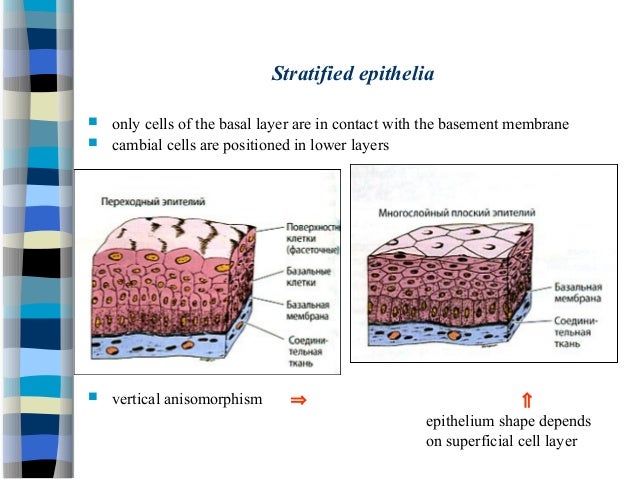
Basement membrane layers of epithelial tissue. The establishment of the correct epithelial polarity and can modulate the phenotype of epithelial cells. It is formed by the association of two layers. Supported by connective tissue all epithelia are supported by connective tissue.
It lies underneath sheets of epithelial cells. Basement membrane pores in human bronchial epithelium. The basement membrane also provides a protective barrier against foreign objects and malignant cells.
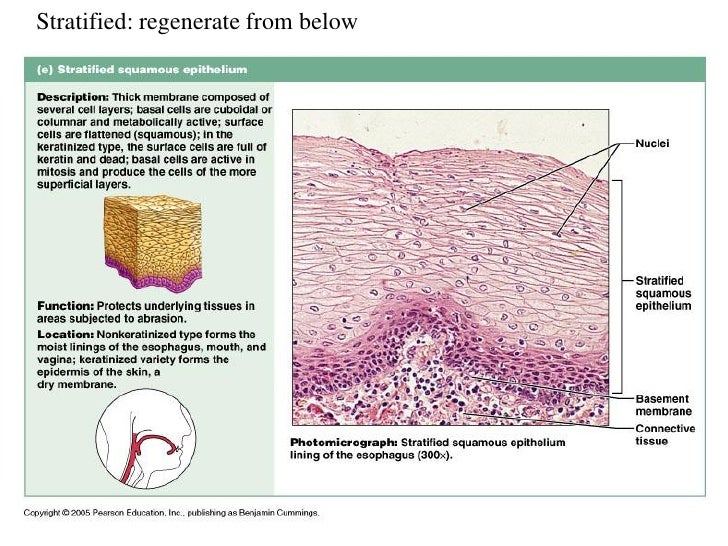
For instance deep to the basal lamina is reticular lamina extracellular material containing collagen protein fiber which forms the basement membrane. Epithelial tissue rests on a basement membrane which acts as a scaffolding on which epithelium can grow and regenerate after injuries. 89 the upper basement membrane layers.
It consists of two parts the basal lamina and the reticular connective tissue underneath. The basement membrane reinforces the epithelium and helps it resist stretching and tearing. The basal lamina lamina layers also known as the basement membrane is a specialised form of extracellular matrix.
45 although the. Epithelial tissue rests on a structure called the basement membrane. Epithelial tissue lines parts of the body that are in contact with the.
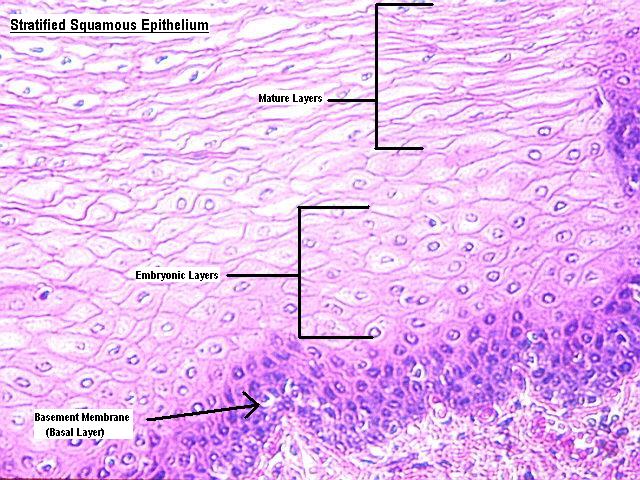
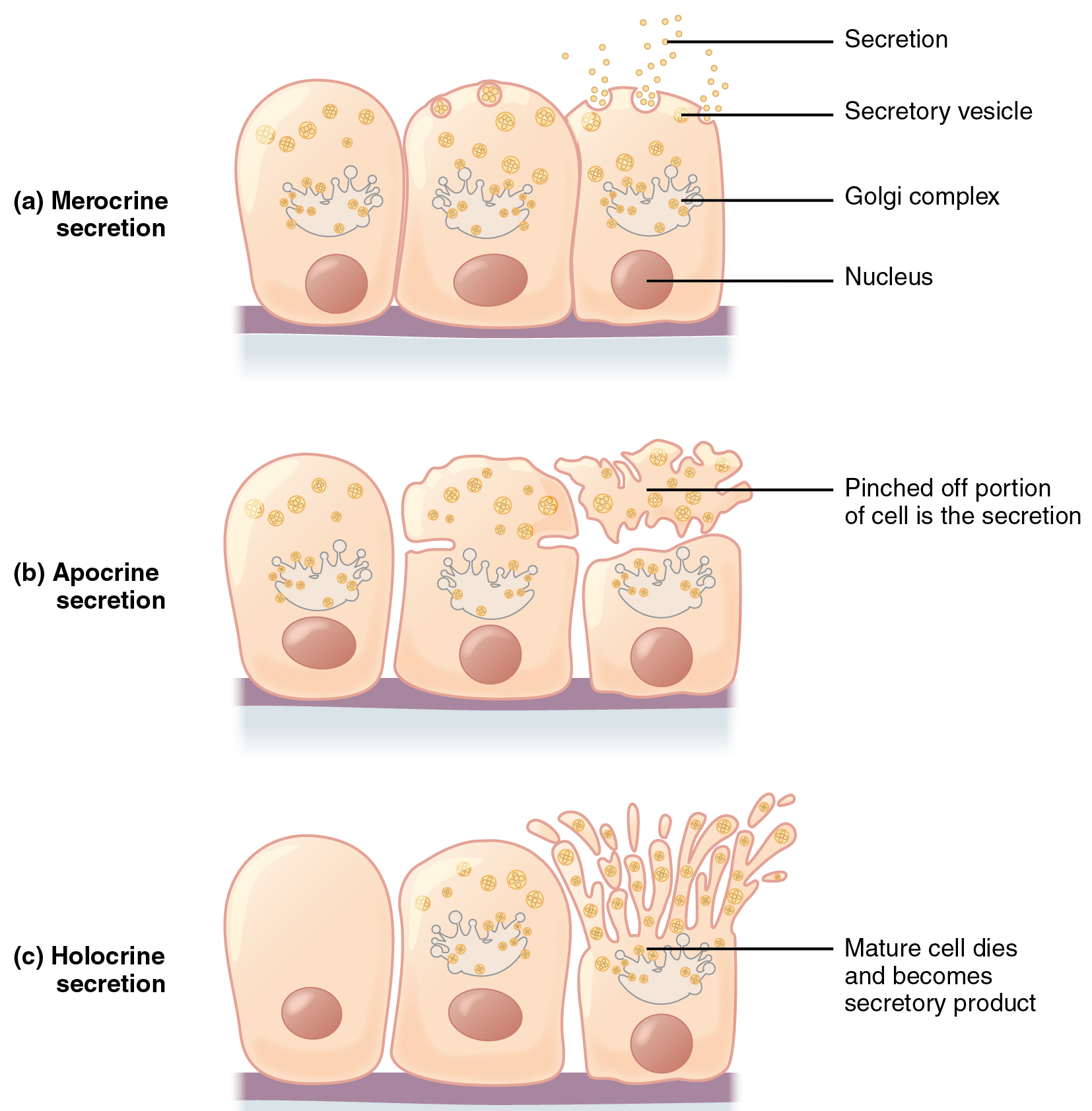
Turnover time is higher for all types of epithelium as compared to connective tissue highest turnover time is a result of the higher level of mitosis in those deepest dividing cells near the basement membrane older superficial epithelial cells are being shed or lost at the same rate as the deeper germinal cells are divided into more cells. The basement membrane bm is a fibrous matrix composed primarily of glycoproteins type iv collagen and laminin that are secreted by the epithelial cells ryerse 1998. The basal lamina can be organised in three ways.
Epithelial tissue has a nerve supply but no blood supply and must be nourished by substances diffusing from the blood vessels in the underlying tissue. The basement membrane is usually visible with the light microscope. As seen with the electron microscope the basement membrane is composed of two layers the basal lamina and the underlying layer of reticular connective tissuethe underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen vii anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrilsthe two layers together are collectively referred to as the basement membrane.
A conduit for. The basal lamina is secreted by the cells of the epithelial tissue itself and contains proteins glycoproteins and collagen iv a type of structural protein that forms sheets. It can surround cells for example muscle fibres have a layer of basal lamina around them.

Histology Various Type Of Epithelium
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ciliated_epithelial_cells-56a09af95f9b58eba4b2031f.jpg)
The Function And Cell Types Of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue Anatomy Physiology

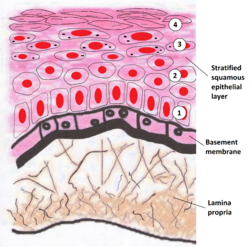
Stratified Squamous Epithelium

Basement Membrane Anatomy Britannica

Simple Squamous Epithelium Google Search Kind Of A Mishmash Of
Epithelial Tissue Objectives Ppt Download

Epithelial Tissue What Is Epithelial Tissue Functions Of
Basement Membrane Lamina Propria
Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands

Basement Membrane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
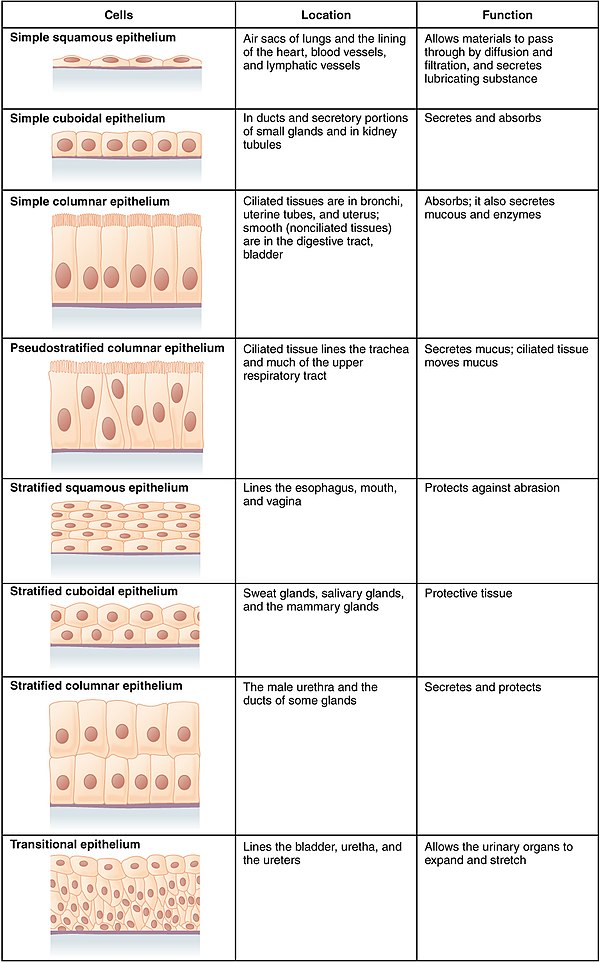
4 2 Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology

A Cross Section Microscopic Image Of Bovine Tongue Epithelium

Respiratory Epithelium Wikipedia



No comments:
Post a Comment